Gérer les conflits au sein des groupes
Cette page a été créée pour aider les personnes militantes à gérer les conflits au sein de leur groupe. Les conflits ont mauvaise réputation, mais ce qui en découle peut être très instructif, et ce qui découle de l'évitement peut nuire à la dynamique et à l'efficacité du groupe. Cette page est un travail en cours qui sera complété au fil du temps. Les informations qu'elle contient proviennent de bases de données existantes sur les organisateurs et de ressources fournies par les mouvement. On y trouve des réflexions sur les raisons pour lesquelles il est important de s'engager dans un conflit, ainsi que des suggestions pour le gérer de manière généreuse.
Pourquoi s'engager dans le conflit?
« La question n'est pas de savoir comment se débarrasser des conflits. La question est de savoir comment l'aborder. » -Rick Hanson
|
Faire place à des pensées/idées divergentes |
Nous ne serons pas toujours d'accord, et nous ne devrions pas l'être. S'engager dans un conflit, c'est inviter de nombreuses perspectives à partager. Un scientifique woke sur Instagram a dit : « Et si nous comprenions que nous n'avons pas besoin que les gens pensent exactement comme nous et soient exactement comme nous pour être AVEC nous et construire avec nous ? » |
|
Développer le pouvoir des uns sur les autres, plutôt que le pouvoir sur les autres. |
Lorsque le pouvoir et la responsabilité sont laissés à eux-mêmes, les conflits sont plus susceptibles de survenir parce que les besoins sont négligés, les gens sont mis à l'écart, etc. Réfléchir à la dynamique du pouvoir et aux privilèges en tant qu'individus dans un contexte de groupe nous aide à comprendre les conflits, à éviter les conséquences évitables et à encourager les conflits génératifs de solutions. |
| Diriger la frustration vers des cibles, et non pas vers nous-mêmes |
|
|
Pour une responsabilisation plutôt qu'une punition |
|
| Comme une occasion de créer des liens et de se regénérer |
La racine du conflit est souvent un désir de connexion. Nous pouvons utiliser le conflit pour nous écouter les uns les autres. |
| Éviter le conflit crée plus de conflit |
L'évitement est une réaction courante aux conflits. Lorsque cela se produit, nous manquons une occasion de nous améliorer et nous donnons au conflit plus d'espace pour se développer et s'étendre. |
Créer des espaces courageux (brave space) qui permettent de gérer les conflits de manière générative
Une invitation aux espaces courageux - Mickey ScottBey Jones [1]
Ensemble nous pouvons créer un espace courageux (brave space)
Parce qu'il n'existe pas d'« espace sûr » (safe space)
We exist in the real world
We all carry scars and we have all caused wounds.
In this space
We seek to turn down the volume of the outside world.
We amplify voices that fight to be heard elsewhere,
We call each other to more truth and love
We have the right to start somewhere and continue to grow.
We have the responsibility to examine what we think we know.
We will not be perfect.
It will not always be what we wish it to be
But
It will be our brave space together,
And
We will work on it side by side.
Care to reduce future harm: a transformative justice approach
What is transformative justice?
“Transformative justice describes a systems approach to identifying root causes of conflict and responding to these as a community – including developing various harm-reduction processes to interpersonal violence within communities at the grassroots level rather than relying on punishment, incarceration, or policing.” -Beyond Survival, edited by Ejeris Dixon and Leah Lakshmi Piepzna-Samarasinha (2020) [2]
Where does transformative justice (TJ) come from?
“TJ was created by and for many of these communities (e.g. Indigenous communities, Black communities, immigrant communities of color, poor and low-income communities, communities of color, people with disabilities, sex workers, queer and trans communities). It is important to remember that many of these people and communities have been practicing TJ in big and small ways for generations–trying to create safety and reduce harm within the dangerous conditions they were and are forced to live in. For example, undocumented immigrant women in domestic violence relationships, disabled people who are being abused by their caretakers and attendants, sex workers who experience sexual assault or abuse, or poor children and youth of color who are surviving child sexual abuse have long been devising ways to reduce harm, stay alive and create safety and healing outside of state systems, whether or not these practices have been explicitly named as “transformative justice.”
We can apply TJ principles to communicating, but it’s important to recognize the origins of TJ are more often than not more intense and challenging than the context of group dynamics where most of us will likely apply this knowledge. If you are dealing with serious harm within your group, see the following wiki page: Notes on accountability from Beyond Survival: Strategies and Stories from the Transformative Justice Movement.
Calling in vs calling out
When a member takes an action that does not reflect the values of the group or breaks the guidelines of group participation, groups may either a) avoid taking action altogether, b) call the person in, or c) call the person out.
| Calling out |
|
|
Calling in |
|
Summary
Another example from Maisha Johnson for Transform Harm: “If my young cousin who’s just taken her first women’s studies class makes a problematic comment, I know calling her in with a conversation or passing her an article might be all the energy I need to expend. Waging a public campaign against her isn’t necessary. But if the problematic behavior is coming from a women’s empowerment organization with a big influence, a more public call-out may be more effective.”
- Use call outs for: applying pressure to power
- Use call ins for: group members and potential recruits
Conflict mapping tool [7]
We can dig deeper into the layers of conflict by exploring 3 key ideas:
- Position: Our initial response, opinion or solution to the conflict (i.e. your stance)
- Interests: what’s important to us in this particular situation, or our concerns or fears about the issue (i.e. your reasoning for your stance).
- Needs: Beneath our interests; universal needs, or the needs that we all have, for example respect, belonging, to be understood etc. (I.e. underlying your reasoning).
Conflict mapping acts as a tool that helps people in conflict form a clearer picture of the issues that are underlying, by exploring these 3 layers. It’s more structured than an open discussion, and makes a conflict conversation easier to facilitate, especially in a group where people are struggling to speak to each other in a civil way. This tool could be facilitated by someone in your group, by a neutral friend or external facilitator. It can be used for conflicts between a few members, or by the whole group. [8]
Steps to conflict mapping
1. Write the issue in the middle of a document (keep it neutral).
2. Add segments surrounding for each person involved in the conflict.
3. Have each person record their position, interests and needs.
4. Invite everyone to look at the map and consider others’ interests and needs that they hadn’t taken into account before.
5. Discuss solutions that consider everyone’s key comments as a team.
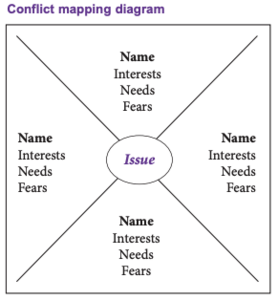
Diagram by: Seeds for Change
Finding solutions to conflicts
There are 4-5 steps for brainstorming solutions to conflicts.
- If relevant, review the group’s mission, vision, agreements for working together etc. to orient members towards a collective solution and/or raise critical reflections about where wrongdoing happened.
- Discuss common points of each person’s position, interests and needs (or if there are none, express understanding)
- Define a compromise that considers everyone’s position, interests and needs.
- Check in that everyone can live with the solution.
- Create an agreement and define how you’ll hold accountability if relevant.
Moving through this process requires trust, and good decision-making processes. See our pages on decision making if needed:
- Consensus decision making 101
- Consensus decision making (suggestions for small groups)
- Modified consensus decision making (suggestions for large and small groups)
- DARCI decision making framework
Si vous avez des corrections ou des ressources complémentaires à nous partager en lien avec ce contenu, vous pouvez contacter florencelehub@proton.me

- ↑ https://www.grossmont.edu/faculty-staff/participatory-governance/student-success-and-equity/_resources/assets/pdf/brave-space-poem.pdf
- ↑ https://brownstargirl.org/beyond-survival/
- ↑ https://inittogether.cargo.site/Section-1
- ↑ https://www.akpress.org/we-will-not-cancel-us.html
- ↑ https://inittogether.cargo.site/Section-1
- ↑ https://inittogether.cargo.site/Section-1
- ↑ https://www.seedsforchange.org.uk/conflictbooklet.pdf
- ↑ https://www.seedsforchange.org.uk/conflictbooklet.pdf